Die Casting vs Investment Casting for Copper Components
Die casting and investment casting serve as two essential methods for producing copper precision components. Each method offers unique benefits and challenges, making the selection process critical for manufacturers. Die casting supports high-volume production with consistent quality, while investment casting enables intricate designs with superior precision. For applications like inlet and outlet chambers-copper Precision Castings, understanding these methods ensures optimal performance and cost-efficiency. The choice directly influences the final product's quality, durability, and suitability for industrial use.
Key Takeaways
Die casting is ideal for high-volume production, offering efficiency and consistent quality for large-scale manufacturing.
Investment casting excels in creating intricate designs and tight tolerances, making it the preferred choice for detailed components.
Choosing the right casting method impacts the final product's quality, durability, and cost-effectiveness, so manufacturers should align their choice with application needs.
Die casting minimizes material waste and labor costs, making it a cost-effective solution for mass production.
Investment casting provides superior surface finishes, often eliminating the need for extensive post-processing.
Understanding the unique properties of copper is crucial, as die casting requires alloys for better castability, while investment casting can handle pure copper effectively.
Manufacturers should consider production volume, design complexity, and cost when deciding between die casting and investment casting.
Understanding Die Casting for Copper Components
Understanding Die Casting for Copper Components
What is Die Casting?
Overview of the die Casting Process
Die casting involves forcing molten metal into a mold cavity under high pressure. Manufacturers use this method to produce components with precise dimensions and smooth surfaces. The process begins by heating the metal until it reaches a liquid state. The molten metal is then injected into a steel mold, also known as a die, which is designed to shape the component. Once the metal solidifies, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected. This technique ensures rapid production and consistent results.
How it works specifically for copper
Copper, known for its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, presents unique challenges in die casting. Its high melting point requires specialized equipment and materials to withstand extreme temperatures. Manufacturers often use alloys, such as copper-zinc or copper-aluminum, to improve castability. The molten copper alloy is injected into the die at high pressure, ensuring the material fills every detail of the mold. This process creates durable components with precise dimensions, suitable for industrial applications.
Advantages of Die Casting for Copper
High production efficiency
Die casting offers unmatched efficiency for large-scale production. The automated nature of the process allows manufacturers to produce thousands of identical components in a short time. This efficiency reduces lead times and ensures timely delivery of products.
Consistent quality for large volumes
The die casting process guarantees uniformity across all components. Each part produced from the same mold maintains identical dimensions and properties. This consistency makes die casting ideal for industries requiring high-quality, standardized parts.
Cost-effectiveness for mass production
Die casting minimizes material waste and reduces labor costs. The reusable molds and automated machinery lower production expenses over time. For high-volume orders, this method proves to be one of the most cost-effective solutions.
Limitations of Die Casting for Copper
Challenges with high melting points of copper
Copper's high melting point poses significant challenges during die casting. The extreme temperatures can cause wear and tear on molds and machinery. Manufacturers must invest in durable materials and advanced equipment to handle these conditions, increasing initial costs.
Limited design flexibility
Die casting works best for simple to moderately complex designs. The rigid molds restrict the ability to create intricate shapes or undercuts. For highly detailed components, alternative methods like investment casting may be more suitable.
Surface finish considerations
While die casting produces smooth surfaces, achieving a flawless finish may require additional post-processing. Surface imperfections, such as porosity or minor defects, can occur due to the rapid cooling of molten copper. These issues may necessitate polishing or coating to meet specific aesthetic or functional requirements.
Understanding Investment Casting for Copper Components
What is Investment Casting?
Overview of the investment casting process
Investment casting, also known as lost-wax casting, involves creating a wax model of the desired component.
How it works specifically for copper
After creating the ceramic mold, molten copper or copper alloy is poured into the cavity.
Advantages of Investment Casting for Copper
High precision and intricate designs
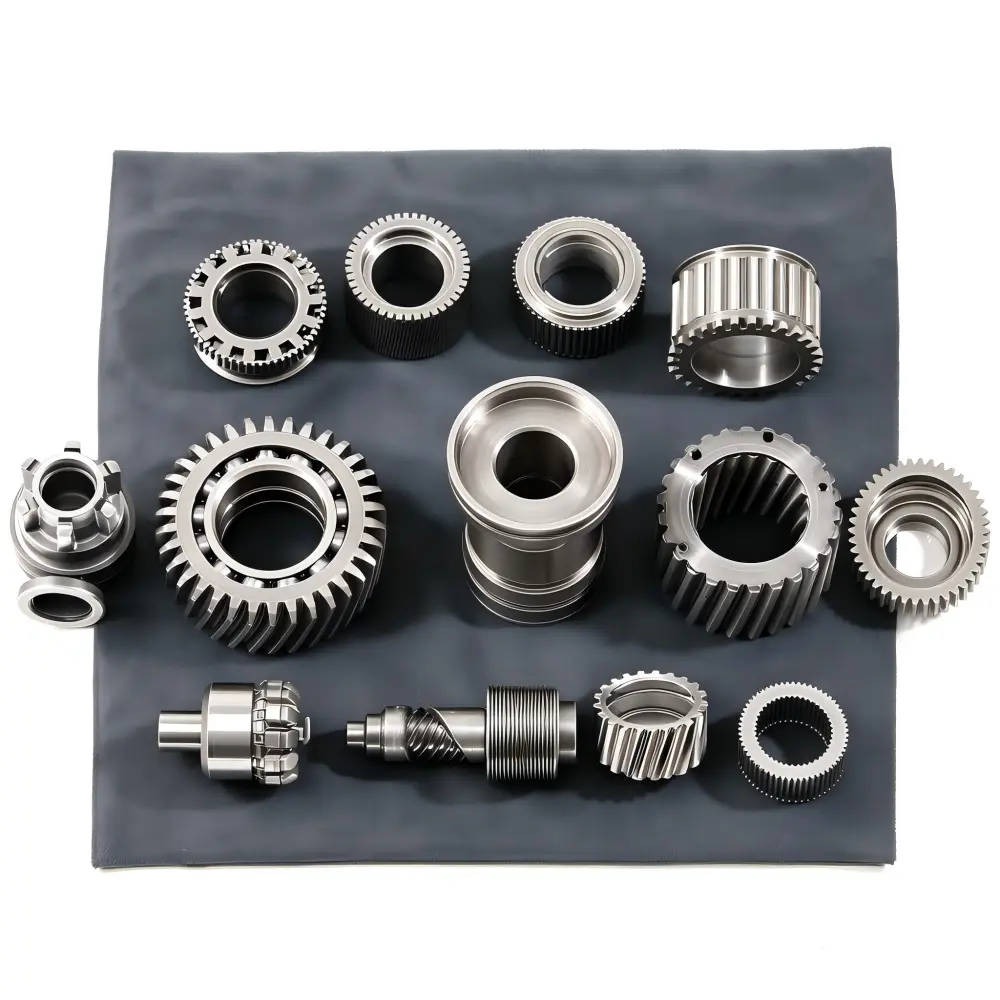
Investment casting excels in producing components with complex geometries and tight tolerances. The wax model allows for the creation of intricate designs that other methods cannot achieve. This precision makes it ideal for applications requiring detailed and customized parts.
Superior surface finish
The ceramic mold used in investment casting provides a smooth surface finish. This eliminates the need for extensive post-processing. The resulting components often require minimal polishing or machining, saving time and resources.
Versatility in design and material use
Investment casting supports a wide range of designs and materials. Manufacturers can create components with varying wall thicknesses, undercuts, and fine details. The process also accommodates different copper alloys, offering flexibility in meeting specific application requirements.
Limitations of Investment Casting for Copper
Higher production costs
Investment casting involves multiple steps, including creating wax models and ceramic molds. These steps increase production costs compared to other methods. The process also requires skilled labor and specialized equipment, further adding to expenses.
Longer production times
The multi-step nature of investment casting results in longer lead times. Each stage, from mold creation to final finishing, requires careful attention to detail. This makes the process less suitable for projects with tight deadlines.
Less suitable for high-volume production
Investment casting is not ideal for large-scale production. The time and cost involved in creating individual molds for each component make it inefficient for high-volume manufacturing. For mass production, methods like die casting offer better efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Comparing Die Casting and Investment Casting for Copper Components
Comparing Die Casting and Investment Casting for Copper Components
Material Compatibility
How each method handles copper's properties
Die casting and investment casting interact with copper in distinct ways due to its unique properties. Copper's high melting point presents challenges for die casting. Manufacturers must use specialized equipment and durable molds to withstand the extreme temperatures required to process copper alloys. This method works best with copper-based alloys like copper-zinc or copper-aluminum, which improve castability and reduce wear on machinery.
Investment casting, on the other hand, handles copper's properties with greater flexibility. The process accommodates pure copper and a wide range of copper alloys. The high fluidity of molten copper during investment casting ensures that even the smallest details of the mold are captured. This makes it an excellent choice for applications requiring precision, such as inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings. The ceramic molds used in investment casting also resist the high temperatures of molten copper, ensuring durability and accuracy.
Design Complexity
Suitability for intricate vs. simple designs
Die casting excels in producing components with simple to moderately complex designs. The rigid steel molds used in this process limit the ability to create intricate shapes or undercuts. While die casting achieves consistent results for straightforward geometries, it struggles with highly detailed or customized designs. Manufacturers often choose this method for parts where design complexity is not a priority.
Investment casting offers unparalleled precision for intricate designs. The wax model used in this process allows for the creation of complex geometries, including thin walls, fine details, and undercuts. This capability makes investment casting ideal for components requiring high levels of customization. For example, manufacturers often rely on this method for intricate parts like inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings, where precision and detail are critical.
Production Volume
Efficiency for small vs. large-scale production
Die casting provides unmatched efficiency for large-scale production. The automated nature of the process enables manufacturers to produce thousands of identical components quickly. Reusable molds and high-speed machinery reduce production time and costs, making die casting the preferred choice for high-volume manufacturing.
Investment casting, however, is better suited for small to medium production runs. The multi-step process, including wax model creation and ceramic mold preparation, requires more time and resources. This makes it less efficient for mass production. However, for smaller batches or specialized components, investment casting delivers superior quality and precision, justifying the longer production times and higher costs.
Cost Considerations
Initial setup costs and per-unit costs
Die casting and investment casting differ significantly in terms of cost structure. Die casting requires a substantial initial investment due to the need for durable steel molds and specialized machinery. These molds, while expensive to produce, are reusable for high-volume production, which reduces the per-unit cost over time. For manufacturers aiming to produce thousands of identical components, this method proves cost-effective in the long run.
Investment casting, on the other hand, involves higher per-unit costs due to its labor-intensive process. The creation of individual wax models and ceramic molds for each component increases production expenses. Additionally, the single-use nature of ceramic molds adds to the overall cost. However, for small production runs or highly detailed components, the precision and quality achieved through investment casting often justify the higher costs.
Surface Finish and Precision
Quality of finish achievable with each method
Die casting delivers components with smooth surfaces and consistent dimensions. However, achieving a flawless finish may require additional post-processing. Surface imperfections, such as porosity or minor defects, can arise due to the rapid cooling of molten copper. Polishing or coating is often necessary to meet specific aesthetic or functional requirements.
Investment casting excels in producing superior surface finishes. The ceramic molds used in this process create components with minimal surface irregularities. This eliminates the need for extensive post-processing. The high level of precision achieved ensures that the final product meets tight tolerances and intricate design specifications. For applications requiring exceptional detail and finish, investment casting stands out as the preferred choice.
Application Example: Inlet and Outlet Chambers-Copper Precision Castings
How die casting and investment casting compare for this specific application
Inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings serve as an excellent example to highlight the differences between these two methods. Die casting offers a cost-effective solution for producing these components in large quantities. The process ensures consistent quality and rapid production, making it suitable for industries requiring standardized parts. However, the limited design flexibility of die casting may restrict its use for highly intricate chamber designs.
Investment casting, in contrast, provides the precision and detail necessary for complex inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings. The ability to capture fine details and achieve tight tolerances makes this method ideal for customized or intricate designs. Although the production costs are higher, the superior surface finish and design versatility often outweigh the expense for specialized applications. Manufacturers seeking high-quality, detailed components frequently choose investment casting for these chambers.
Choosing the Right Casting Method for Your Application
When to Choose Die Casting
Applications requiring high-volume production
Die casting proves ideal for projects demanding large-scale production. Manufacturers often rely on this method when producing thousands of identical components within tight deadlines. Its automated process ensures rapid output without compromising consistency. Industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods benefit significantly from die casting due to its ability to deliver standardized parts efficiently. For example, automotive manufacturers use die casting to produce engine components, housings, and brackets in bulk.
Examples of industries and use cases
Several industries leverage die casting for its efficiency and cost-effectiveness. The automotive sector uses it extensively for lightweight yet durable parts. Electronics manufacturers depend on die casting to create enclosures and heat sinks that require precise dimensions. In the consumer goods industry, this method supports the production of items like kitchen appliances and hardware. For applications like inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings, die casting offers a practical solution when high-volume production is a priority.
When to Choose Investment Casting
Applications requiring precision and complexity
Investment casting excels in scenarios where precision and intricate designs are essential. This method allows manufacturers to produce components with complex geometries and tight tolerances. It becomes the preferred choice for projects requiring detailed customization or superior surface finishes. Industries such as aerospace, medical, and energy sectors often select investment casting for critical components. For instance, turbine blades, surgical instruments, and valve bodies benefit from the precision and quality achieved through this process.
Examples of industries and use cases
Industries requiring high-performance components often turn to investment casting. The aerospace sector uses it to manufacture parts like turbine blades and structural components with intricate designs. Medical device manufacturers rely on investment casting for surgical tools and implants that demand exceptional accuracy. In the energy industry, this method supports the production of components like pump housings and valve bodies. For specialized applications such as inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings, investment casting ensures the level of detail and quality necessary for optimal performance.
Die casting and investment casting offer distinct advantages for copper components. Die casting excels in high-volume production, delivering cost-effective and consistent results. Investment casting, however, provides unmatched precision and intricate detailing, making it ideal for complex designs. Manufacturers must align their choice with the specific needs of their application. For example, inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings benefit from investment casting’s superior surface finish and detail, while die casting supports large-scale production efficiently. Selecting the right method ensures optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and product quality.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between die casting and investment casting?
The primary difference between die casting and investment casting lies in their applications and capabilities.
Which method is more cost-effective for copper components?
Die casting proves more cost-effective for large-scale production due to its reusable molds and automated process. Investment casting, while more expensive, offers better precision and surface finish, making it ideal for smaller production runs or highly detailed components.
Can both methods handle pure copper?
Investment casting handles pure copper more effectively due to its ability to accommodate high fluidity and capture fine details. Die casting often requires copper alloys, such as copper-zinc or copper-aluminum, to improve castability and reduce wear on molds.
Which casting method provides better surface finish?
Investment casting delivers a superior surface finish due to the use of ceramic molds, which minimize surface irregularities. Die casting may require additional post-processing, such as polishing or coating, to achieve a comparable finish.
What are the limitations of die casting for copper components?
Die casting faces challenges with copper's high melting point, which can cause wear on molds and machinery. It also offers limited design flexibility and may require post-processing to address surface imperfections.
Is investment casting suitable for high-volume production?
Investment casting is less suitable for high-volume production due to its labor-intensive and time-consuming process. It works best for small to medium production runs or applications requiring intricate designs and tight tolerances.
How do manufacturers decide between die casting and investment casting?
Manufacturers consider factors like production volume, design complexity, cost constraints, and required surface finish. Die casting is chosen for high-volume, standardized parts, while investment casting is preferred for detailed and customized components.
What industries commonly use die casting for copper components?
Industries such as automotive, electronics, and consumer goods frequently use die casting. It supports the production of engine components, heat sinks, and hardware that require consistent quality and rapid manufacturing.
What are the typical applications of investment casting for copper components?
Investment casting is widely used in aerospace, medical, and energy industries. It produces turbine blades, surgical instruments, and valve bodies that demand exceptional precision and intricate designs.
Can both methods be used for inlet and outlet chambers-copper precision castings?
Yes, both methods can produce inlet and outlet chambers. Die casting offers a cost-effective solution for large quantities, while investment casting ensures superior detail and surface finish for intricate designs. The choice depends on the specific requirements of the application.