Precision Casting is a remarkable technique in manufacturing that ensures high-quality results. It offers detailed and intricate shapes that traditional methods may struggle to achieve. This method utilizes molten metal poured into precise molds, creating components with exceptional accuracy.
However, the process is not without challenges. Achieving the perfect temperature is crucial. If not managed well, defects can arise. The quality of the mold also significantly impacts the final product. Investing in high-grade materials is essential for minimizing errors.
Moreover, while Precision Casting can produce fine details, it demands a meticulous approach. Skilled technicians are needed at various stages. Attention to detail is paramount. Any oversight can compromise the integrity of the finished piece. With careful practices, manufacturers can fully harness the benefits of Precision Casting for superior outcomes.
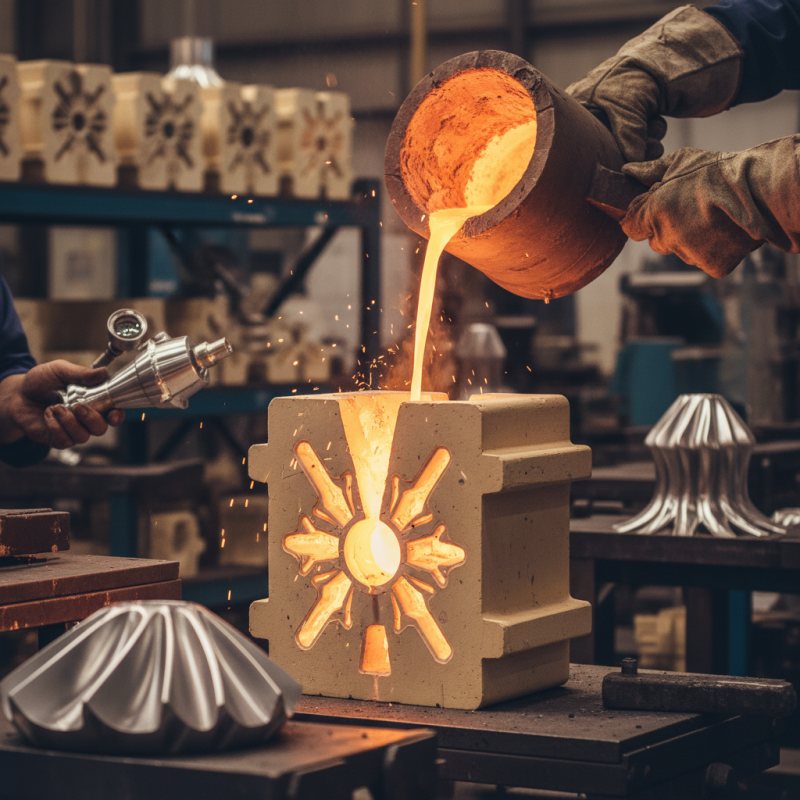

Precision casting is a manufacturing process that creates high-quality components. It allows for intricate designs with a high level of detail. This method involves pouring molten metal into a mold that accurately shapes the end product. The result is a near-net shape, reducing the need for extensive machining.
One key benefit of precision casting is its ability to produce complex geometries. It can create shapes that other methods struggle with. This capability saves time and material. However, this process requires careful planning. If not executed correctly, it may lead to defects. These imperfections can impact the final product's quality.
Another advantage is the excellent surface finish that precision casting provides. Components often require minimal surface treatment. This reduces additional processing time. However, achieving the desired finish may require rigorous quality control. Regular checks are essential to maintain high standards. Balancing efficiency with quality can be challenging in this method.
Precision casting is a sophisticated process used in high-quality manufacturing. It allows for the production of complex shapes with high dimensional accuracy. The process begins with creating a wax or plastic pattern. This pattern is then coated with a ceramic shell. After hardening, the shell is heated to remove the pattern, leaving a hollow mold. This step often reveals imperfections that need careful review.
Next, molten metal is poured into the mold. The precision of this step is crucial. In a recent industry report, it was found that over 30% of casting defects stem from improper filling techniques. Pouring at the right temperature and speed can help mitigate these issues. Once cooled, the mold is broken away, revealing the final product. Post-processing may involve sanding and machining to achieve the desired finish.
Quality control is vital throughout the process. Experts suggest that 90% of companies using precision casting achieve significant cost savings. However, challenges remain. Variations in material properties can lead to inconsistencies. Regular testing and evaluation are necessary to ensure reliability. Engaging in these steps fosters improvements and highlights the importance of ongoing assessment in the precision casting industry.
| Step | Description | Materials Used | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Create a Wax Model | Wax | Prototype Development |
| 2 | Make a Ceramic Mold | Ceramics | Complex Shapes |
| 3 | Remove Wax | Heat Source | Mold Prepping |
| 4 | Pour Metal | Steel, Aluminum, Bronze | Manufacturing Parts |
| 5 | Cooling Process | N/A | Solidification |
| 6 | Remove Mold | N/A | Part Extraction |
| 7 | Finishing Touches | Polishing Tools | Quality Control |
Precision casting plays a vital role in high-quality manufacturing. Choosing the right materials is crucial for achieving desired outcomes. Common materials include aluminum alloys, bronze, and stainless steel. Each brings unique properties to the final product.
Aluminum alloys are lightweight yet strong. They offer excellent resistance to corrosion. However, they may not withstand extreme temperatures. Bronze is known for its durability and excellent wear resistance. It's ideal for intricate designs. Still, it might be more expensive and harder to source. Stainless steel is robust and adaptable, but it can be challenging to cast with high precision.
Understanding the properties of these materials is essential. Assessing how they behave under different conditions can lead to better results. Sometimes, the choice of material may seem obvious, but unexpected issues arise. For example, some materials may require advanced techniques to mold properly. This can lead to frustration in the manufacturing process. Innovations in material science can further enhance quality, yet experimenting with new options often comes with risks. Balancing these factors is part of the challenge in precision casting.
Quality control measures are essential in precision casting. This process requires meticulous attention at every stage. First, understanding the materials used is crucial. Not all alloys perform the same. Their composition can affect the final product's integrity and durability. A random selection of samples for testing increases the risk of undetected flaws.
Temperature management plays a vital role. The pouring temperature must be controlled carefully. Overheating can lead to defects like porosity. Monitoring cooling rates is equally important. Too fast can cause cracks, while too slow can lead to uneven structures. Regular inspections during these phases can pinpoint potential issues.
Documentation should be rigorous. Tracking every step can help identify where problems arise. However, it’s not always possible to catch every defect. Sometimes, flaws only appear after production. Continuous improvement is vital. Teams should regularly review outcomes and update processes based on findings. Open discussions about mistakes can lead to better practices in the future.
Precision casting is a versatile process found in many industries. It allows for intricate designs and high precision that traditional methods struggle to achieve. In the automotive sector, precision casting molds critical engine parts that require durability and accuracy. These components often face extreme conditions. Therefore, the need for reliable manufacturing methods is evident.
In the aerospace field, precision casting is pivotal as well. Aircraft components made using this method can meet high-performance standards. However, the complexity of designs can sometimes lead to defects. Rigorous testing and quality control are essential but can be overlooked amidst tight deadlines. This creates a need for continuous improvement.
Medical devices also benefit from precision casting. Custom parts can be tailored to specific needs, improving patient outcomes. Yet, challenges exist in maintaining consistency across batches. Fluctuations in material quality may cause discrepancies. Manufacturers must remain vigilant to ensure safety and efficacy.






