Copper Precision Casting is a vital process in manufacturing high-quality metal parts. It requires a careful approach to achieve the best results. Mistakes in this process can lead to defects. Understanding the intricacies of this technique is crucial.
Attention to detail is key in Copper Precision Casting. The quality of molds can impact the final product. Proper temperature control and alloy selection are also essential. Each step of production demands focus and precision. Yet, many overlook these aspects, leading to unsatisfactory outcomes.
Learning from past experiences is important for improvement. Analyzing failures can reveal insights into better practices. Embracing a culture of reflection can enhance the quality of casting. With the right mindset, one can master Copper Precision Casting for optimal results.
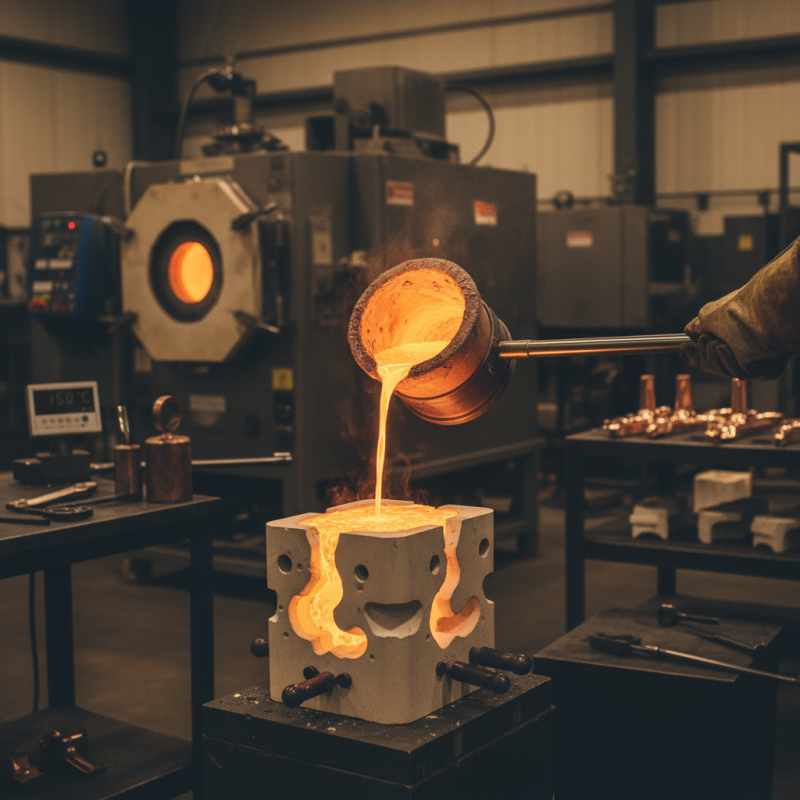

Copper precision casting is a vital process in various industries. This technique allows for the production of intricately designed components with high dimensional accuracy. Applications span across sectors such as electronics, automotive, and aerospace. According to a recent industry report, the global copper casting market is projected to reach $20 billion by 2026, reflecting a growing demand for high-quality copper parts.
The versatility of copper makes it ideal for applications requiring excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance. For instance, in the electronics sector, copper casts are essential for creating connectors and heatsinks. Notably, the manufacturing process can be challenging. While precision is key, issues with porosity and uneven surfaces can occur. Addressing these imperfections requires careful control of the melting and cooling processes.
In automotive applications, copper components are increasingly used for electric vehicles. A study indicates that about 50% more copper is needed in electric cars compared to traditional vehicles. This trend highlights the importance of effective casting methods. However, not all casting operations are optimized. Many systems still lack the technology to monitor quality in real-time, leading to reduced efficiency and higher costs.
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Material Selection | Choose high-purity copper alloys to enhance mechanical properties. |
| Mold Design | Ensure molds have proper gating and riser systems for efficient casting. |
| Temperature Control | Maintain optimal melting and pouring temperatures to minimize defects. |
| Heat Treatment | Apply heat treatment post-casting to improve strength and ductility. |
| Surface Finish | Consider additional finishing processes for improved aesthetics and performance. |
| Quality Control | Implement rigorous quality control measures throughout the casting process. |
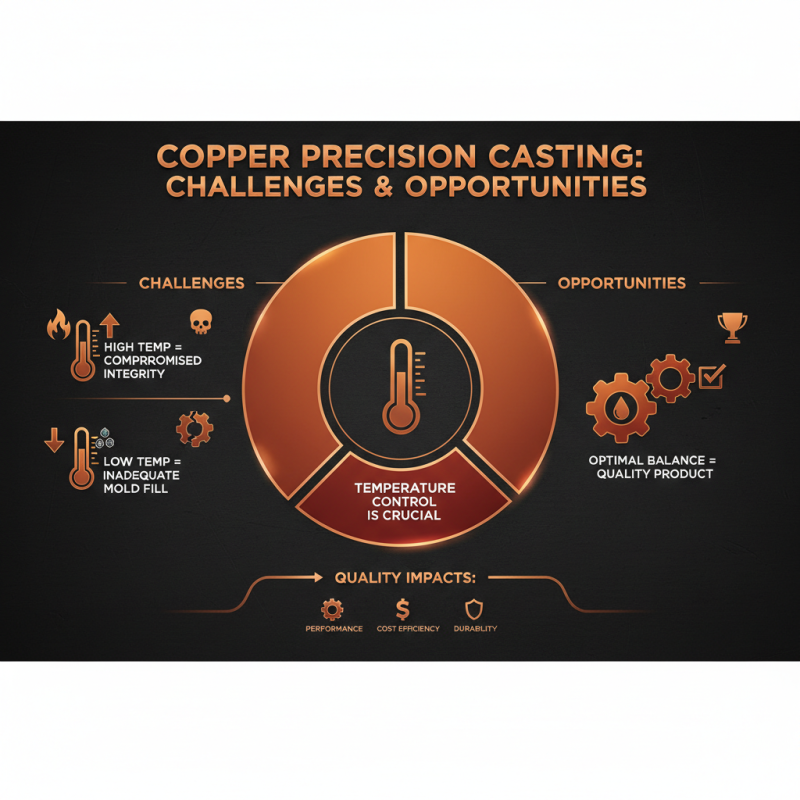
Copper precision casting offers unique challenges and opportunities. Several factors can greatly impact the quality of the final product. Temperature control is crucial during the melting process. If temperatures are too high, the integrity of the copper may be compromised. Conversely, too low temperatures can lead to inadequate mold filling. Finding the right balance is vital for optimal results.
Another key factor is mold design. The complexity of the mold can affect how smoothly the molten copper flows. Intricate designs might trap air, causing defects in the final piece. Additionally, surface finish plays an important role. A rough surface can create weak points in the cast. Quality control during the finishing process is essential. This stage often reveals overlooked imperfections and areas for improvement.
Worker experience cannot be underestimated. Skilled operators are essential for navigating the complexities of copper casting. Their ability to adjust processes in real time can directly influence outcomes. Inadequate training or lack of attention can lead to repeated mistakes. Each of these elements contributes to overall quality, emphasizing the need for careful evaluation and constant improvement.
Copper precision casting is a detailed process requiring careful execution. Preparing the mold is essential. It starts with selecting high-quality materials. The mold must withstand high temperatures. Ensure the design is precise to avoid defects. Once the mold is ready, a thorough cleaning is crucial. Dust and debris can affect the final product's quality.
Next, we melt the copper. This step requires attention to temperature. Too hot, and the copper can become too fluid. Too cool, and it won’t fill the mold properly. Pouring must be done carefully and steadily. Any sudden movements can cause bubbles or inconsistencies. After pouring, allow the mold to cool naturally. Quenching can warp the shape.
After cooling, it's time for the finishing touches. This stage often reveals imperfections. Minor flaws might appear, requiring polishing or additional machining. It's important not to rush this process. Each step matters in achieving optimal results. Always remember that practice and patience lead to improvement. Reflect on each casting experience to enhance your technique.
Copper precision casting presents unique challenges that require careful attention. One common issue is the formation of porosity. This defect occurs when gases get trapped in the molten copper, leading to weak spots in the final product. To combat this, proper vacuum techniques can be utilized. Additionally, ensuring optimal melting temperatures can significantly reduce gas formation.
Another challenge is achieving dimensional accuracy. Copper castings often warp during cooling, and this distortion can compromise the final product. To minimize warping, slow cooling processes should be employed. It’s beneficial to use controlled temperature environments. Careful setup and monitoring are essential for success.
Moreover, surface finish can become a concern. Copper typically requires additional processing to achieve the desired look. Rough surfaces may need polishing or further machining. It’s vital to assess initial casting quality; not every piece will meet standards. Regular checks and adjustments in the process can help improve outcomes.
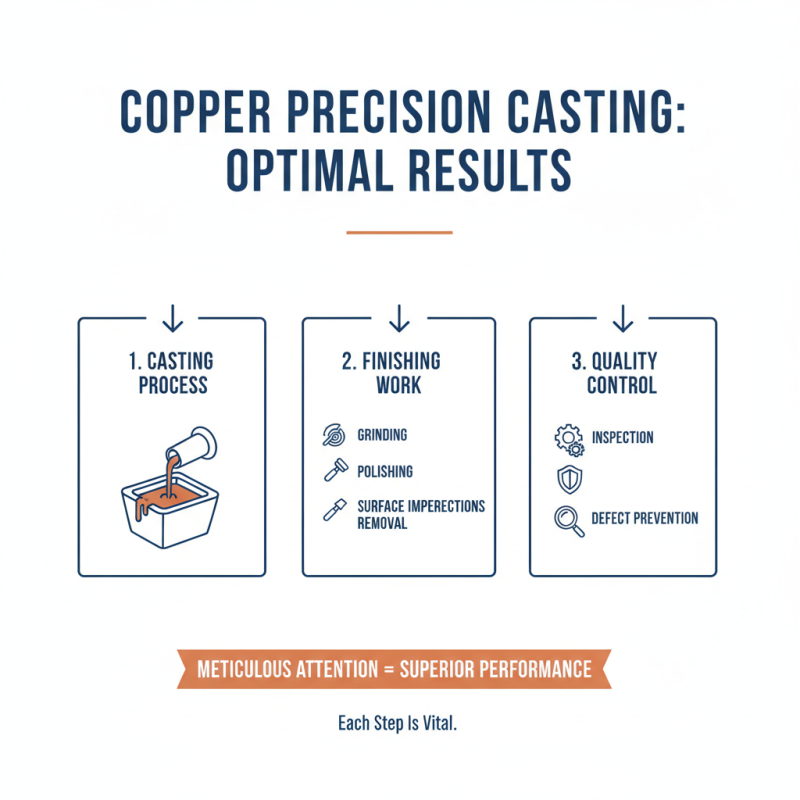
Achieving optimal results in copper precision casting requires meticulous attention to finishing and quality control. After the casting process, components often need significant finishing work. This includes grinding, polishing, and removing any surface imperfections. Each step is vital. A small oversight can lead to defects that affect performance.
Quality control is essential at every stage. Regular monitoring during casting helps catch issues early. Inspect the molds carefully. Look for signs of wear or damage. After casting, check the dimensions and tolerances rigorously. This ensures a perfect fit for assembly.
Another critical area is documentation. Keeping detailed records of each batch is important. It helps identify patterns and potential improvements. Mistakes happen, and reflecting on them can lead to breakthroughs in processes. Quality control isn't just about passing tests; it's about fostering a culture of continuous improvement in manufacturing practices.






